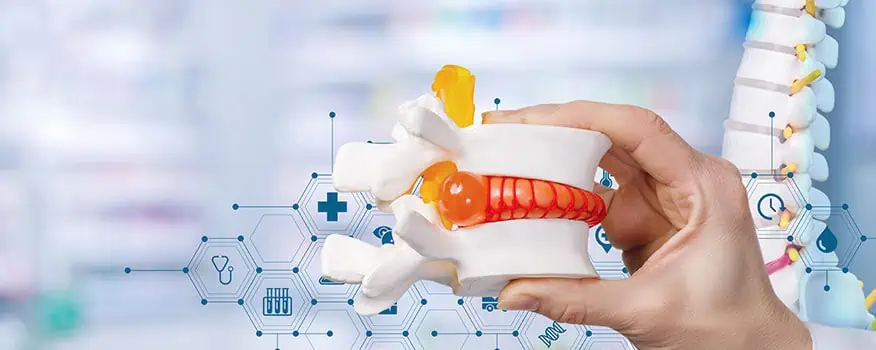
Herniated discs, also known as slipped discs or ruptured discs, are a prevalent spinal condition that can cause severe pain and discomfort. The condition occurs when the gel-like center of a spinal disc protrudes through its outer layer, pressing against nearby nerves. This compression can lead to radiating pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
THE ANATOMY OF SPINAL DISCS
To comprehend herniated discs, it is essential to understand the structure of spinal discs. These discs are soft, circular cushions located between the vertebrae, acting as shock absorbers and allowing for flexibility in the spine. Each disc consists of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a gel-like inner core called the nucleus pulposus. Herniation occurs when the annulus fibrosus weakens or tears, causing the nucleus pulposus to push out of its normal position.
CAUSES OF HERNIATED DISCS
Several factors can contribute to the development of herniated discs. Common causes include:
Age-related Wear and Tear: As we age, the spinal discs lose moisture and become less flexible, making them more susceptible to herniation.
Trauma or Injury: Sudden, forceful impact to the spine, such as from a fall or accident, can cause a herniated disc.
Repetitive Strain: Certain occupations or activities that involve repetitive movements or heavy lifting can put increased stress on the spine, leading to herniated discs over time.
Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to develop herniated discs due to differences in the structure of their spinal discs.
RECOGNIZING THE SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on its location and the nerves affected. Common signs of a herniated disc include:
Radiating Pain: Pain that radiates from the spine to the extremities, such as the legs or arms.
Numbness and Tingling: Patients may experience numbness or tingling sensations in the affected area or extremities.
Muscle Weakness: Herniated discs can lead to muscle weakness, making it challenging to lift or hold objects.
Bowel or Bladder Dysfunction: In severe cases where the herniated disc compresses the nerves severely, it can cause bowel or bladder control problems, requiring immediate medical attention.
UNDERSTANDING THE DIAGNOSTIC PROCESS
Diagnosing a herniated disc involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The process typically includes:
Medical History: The doctor will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, their onset, and any potential contributing factors.
Physical Examination: The physician will conduct a thorough physical examination, assessing reflexes, muscle strength, and areas of pain or discomfort.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans can provide detailed images of the spine, revealing any herniated discs or nerve compression.
Electromyography (EMG): In some cases, an EMG test may be performed to evaluate the electrical activity of muscles and identify nerve damage.
DISTINGUISHING HERNIATED DISCS FROM OTHER CONDITIONS
Herniated discs share symptoms with various other spinal conditions, making it essential to distinguish them accurately. Some conditions that may mimic herniated discs include:
Degenerative Disc Disease: This condition involves the gradual deterioration of spinal discs and can cause pain and stiffness.
Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to nerve compression and similar symptoms to herniated discs.
Sciatica: Sciatic nerve compression can cause radiating pain similar to herniated discs.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENTS FOR HERNIATED DISCS
In many cases, herniated discs can be effectively managed with conservative treatments, which may include:
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding strenuous activities and providing the spine with adequate rest can help reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches can improve flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and alleviate pressure on the affected nerves.
Understanding herniated discs is crucial for early detection and appropriate management of this common spinal condition. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic methods, individuals can seek timely medical attention, allowing for effective treatment and a better quality of life.
To find out more information, contact Joint & Spine Rehabilitation today at (201) 445-1079.