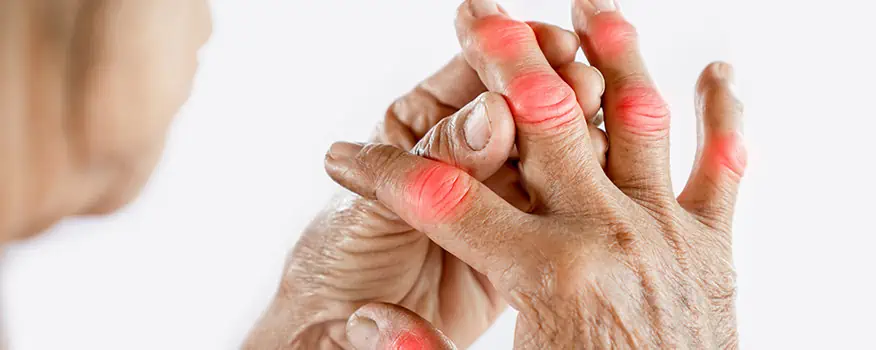
Arthritis is a prevalent and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people around the world. It refers to a group of disorders that involve inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While arthritis is commonly associated with the elderly, it can affect people of all ages, including children.
TYPES OF ARTHRITIS
There are over 100 types of arthritis, each with its own distinct characteristics and causes.
The most common types include:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most prevalent form of arthritis, primarily affecting older adults. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced joint flexibility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to mistakenly attack the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This results in inflammation, joint pain, and eventually joint damage.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): PsA is a form of arthritis that often occurs in individuals with psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. PsA can affect the joints and cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA): JIA refers to arthritis that occurs in children under the age of 16. It can have varying degrees of severity and affect one or more joints.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: This type of arthritis primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, leading to stiffness and pain in the lower back and hips.
- Gout: Gout is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, resulting in sudden and severe episodes of joint pain, most commonly in the big toe.
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF ARTHRITIS
While symptoms can vary depending on the type of arthritis, some common signs include:
- Joint pain, tenderness, and swelling
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- Reduced range of motion
- Warmth and redness around affected joints
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Deformities in advanced cases
IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DETECTION
Detecting arthritis in its early stages is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. Early intervention can help prevent further joint damage, reduce pain, and slow the progression of the disease.
Here’s why early detection matters:
- Preservation of Joint Function: By identifying arthritis early, healthcare providers can recommend appropriate treatments and therapies to preserve joint function and mobility.
- Pain Management: Early treatment can help alleviate pain and discomfort, enabling individuals to engage in daily activities more comfortably.
- Preventing Joint Damage: Some forms of arthritis, like RA, can lead to joint damage and deformities if left untreated. Early intervention can help prevent irreversible damage.
- Tailored Treatment Plans: Identifying the specific type of arthritis allows healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs of each individual.
- Better Long-Term Outcomes: Treating arthritis in its early stages can lead to better long-term outcomes, allowing individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
If you’re experiencing joint pain or other symptoms of arthritis, it’s important to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider will typically conduct a thorough physical examination, review your medical history, and may order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to assess the condition of your joints.
Treatment options for arthritis vary based on the type and severity of the condition.
They may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and corticosteroids can help manage inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can improve joint function, strengthen muscles, and enhance mobility.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and adopting joint-friendly habits can contribute to managing arthritis symptoms.
- Assistive Devices: Braces, splints, and other devices can provide support to affected joints and alleviate strain.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases where other treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions such as joint replacement may be considered.
Understanding arthritis, its types, and the importance of early detection is essential for managing this complex condition. Whether you’re dealing with occasional joint pain or chronic discomfort, remember that medical professionals are equipped to provide guidance, support, and tailored solutions for your unique needs.
If you or a loved one are suffering from arthritis in Waldwick, NJ call us today at (201) 445-1079 to schedule a free consultation.